Remanufacturing

Remanufacturing
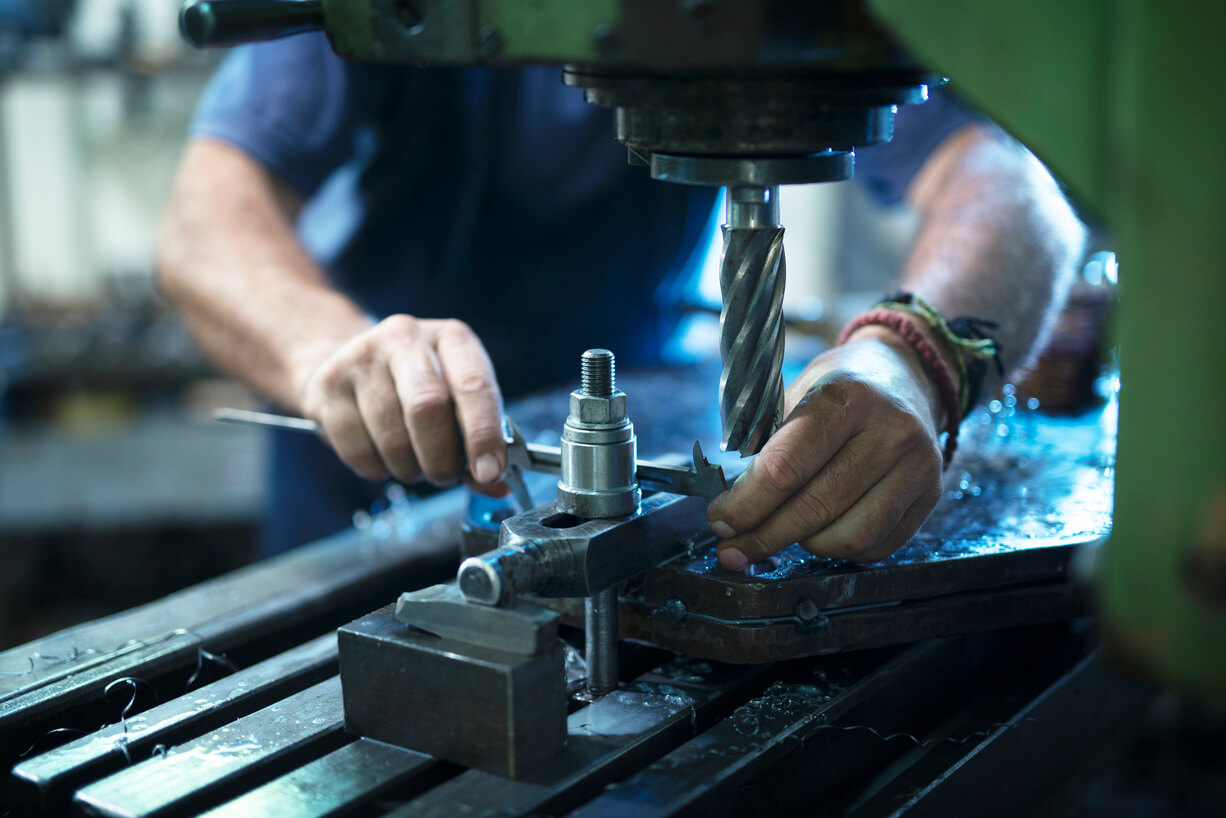
Remanufacturing is a comprehensive and rigorous industrial process by which a previously sold, worn, or non-functional product or component is returned to a “like-new” or “better-than-new” condition with a warranty that guarantees a level of performance and quality.
Remanufacturing is not the same as “recycling” or “repairing”. A lack of awareness of remanufacturing and its benefits by dealers, customers and policymakers remains a major obstacle to growth of the industry.
Benefits of remanufacturing include:
Reduced energy consumption during manufacturing
Reduced waste (and associated disposal costs)
Lower price for comparable quality
Medical equipment
Restaurant and food-service equipment
Conservation of materials (of increasing importance as raw materials become scarcer and more expensive)
Commonly remanufactured product categories are:
Aircraft components
Automotive parts
Electrical and electronic equipment
Engines and components
Printing equipment
Remanufacturing is an important component of a resource-efficient manufacturing industry. By keeping components and their embodied material in use for longer, significant energy use and CO2emissions to air and water can be reduced. In addition to improving resource management, remanufacturing provides opportunities for the creation of highly skilled jobs and economic growth.
Remanufacturing – An Economic Function of the Circular Economy
So what’s different between the life cycle of the newly manufactured product and the remanufactured one? The new product is made entirely from new raw materials, and follows the dominant economic model of our day, a linear economy. Products are made with raw materials, they are consumed, and many end up as waste once they are discarded. Some products and materials are widely recycled and returned back to the early stages of manufacturing.
However, recycling used components means much of the energy and value they embody is lost. In contrast, the remanufactured transmission follows a circular-economy model that looks to design reuse into an economy while phasing waste out of it. This means that end-of-use-cycle products and components are brought back into the economy as inputs to the remanufacturing process to produce newly remanufactured products. While a remanufactured product will likely contain some new parts and cannot be reprocessed indefinitely, it significantly reduces the need for virgin primary natural resources and the amount of waste that is generated.

The Knowledge Centre
Our Knowledge Centre holds an extraordinary amount of information, including research, reports and articles covering more than 50 different topics, including finance, ideas, legal, metrics and monitoring, policy and presentations, as well as images, infographics and movies






